- Industry Challenges in Solid-Liquid Separation
- Mechanical Design & Operational Superiority
- Performance Benchmark: Leading Manufacturers Compared
- Adaptive Engineering for Specific Scenarios
- Industrial Implementation Case Studies
- Maintenance Protocols & Lifecycle Optimization
- Future-Ready Screening Solutions

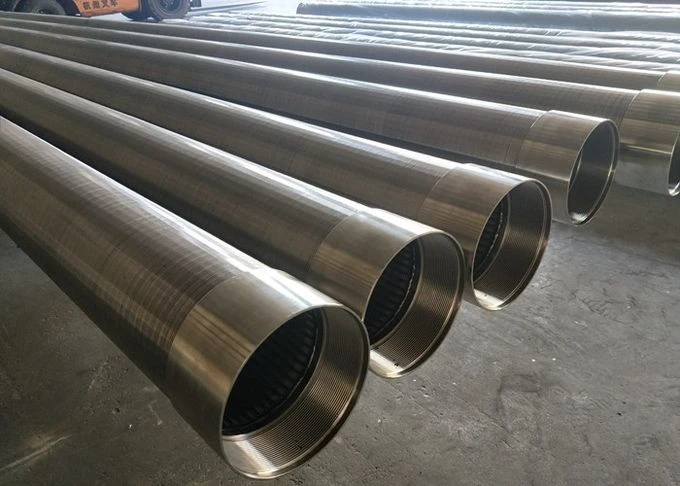
(wastewater treatment screen)
Addressing Critical Needs in Wastewater Treatment Screen Applications
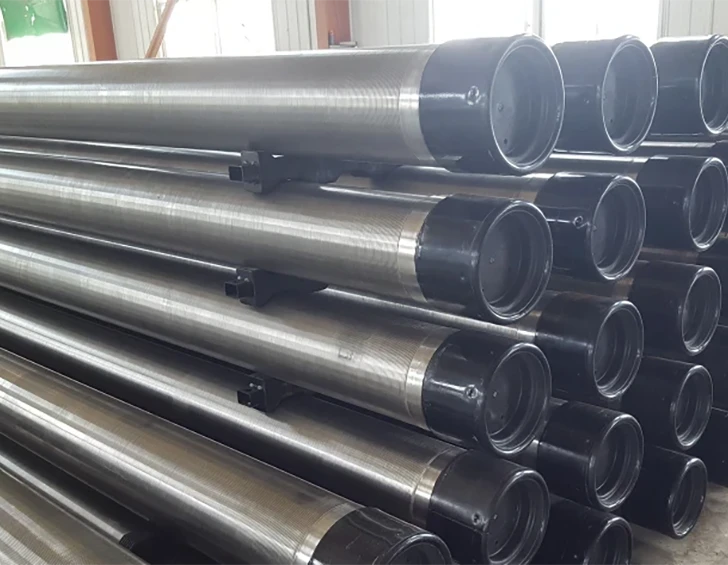
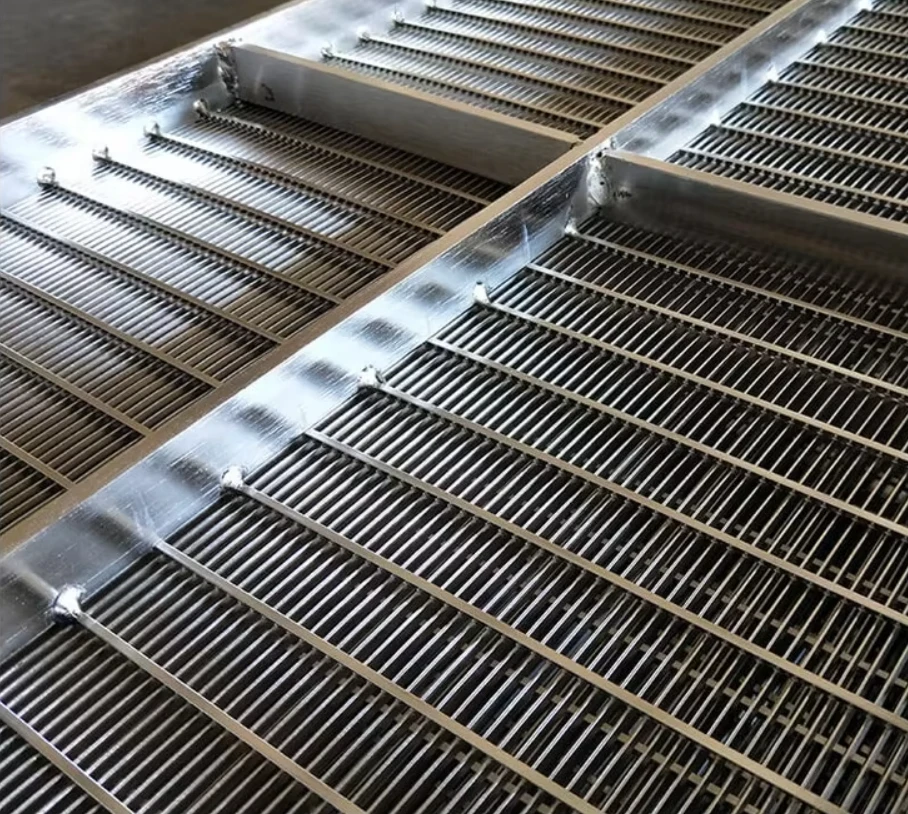
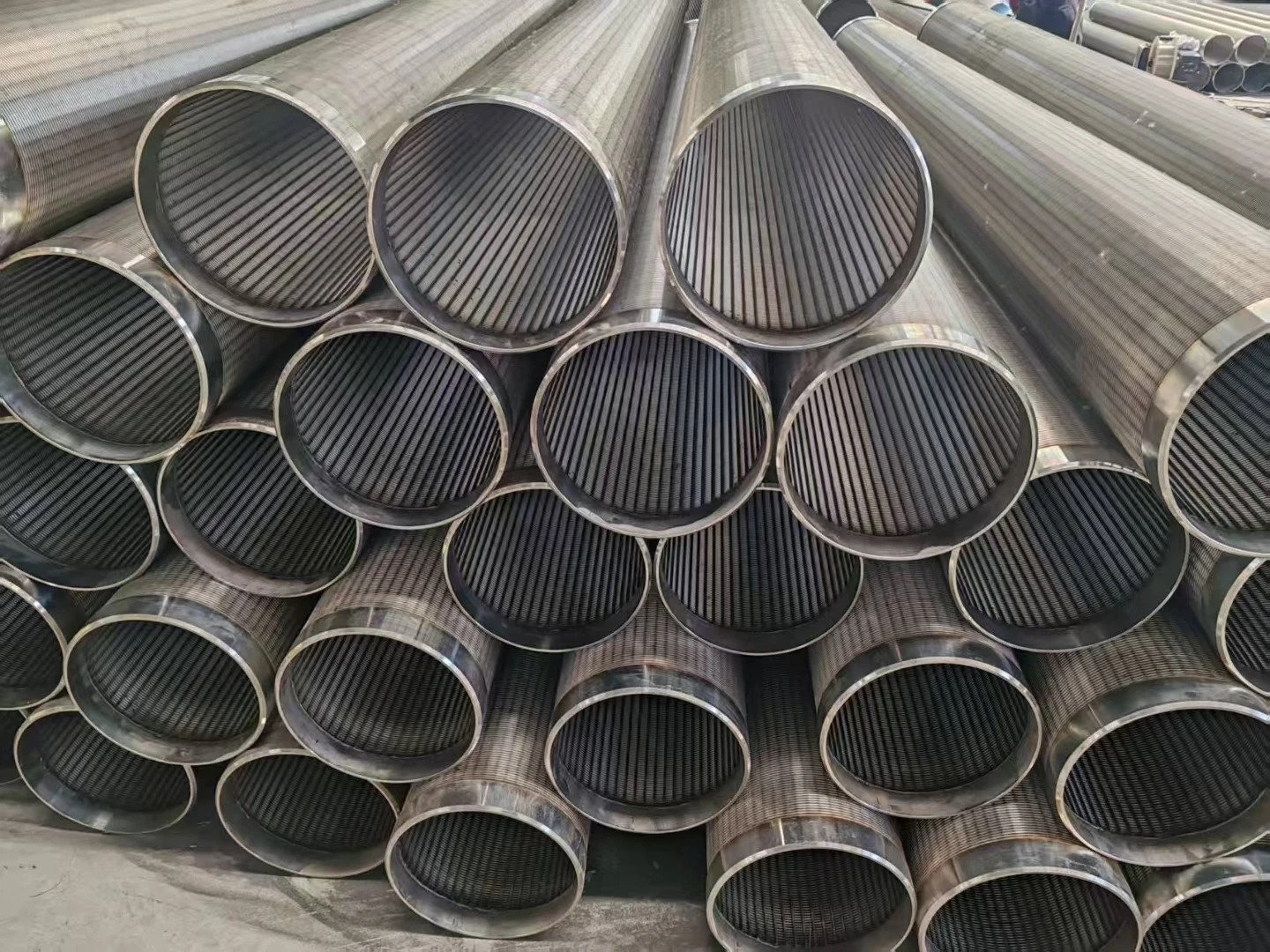
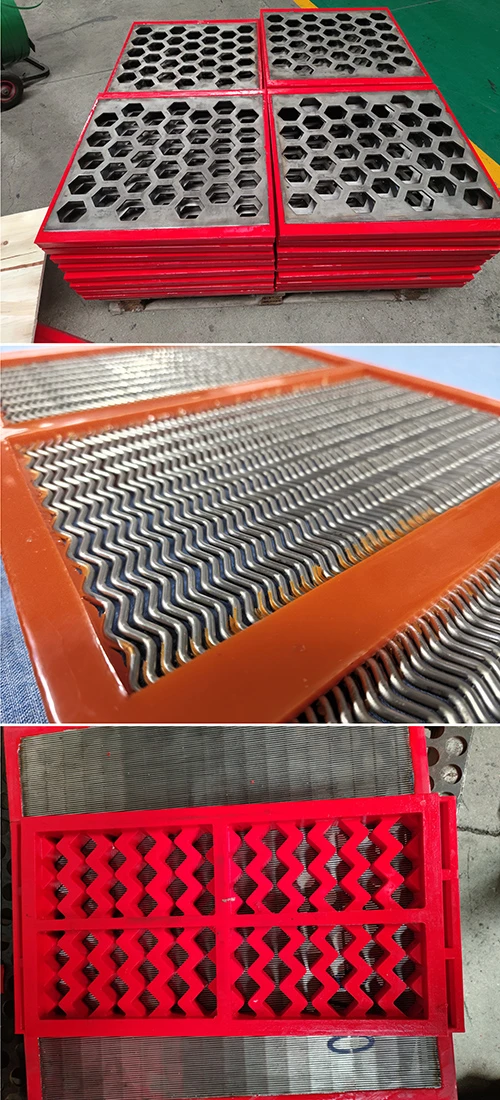
Modern wastewater facilities process 50-800 million gallons daily (EPA 2023), with 23% of operational bottlenecks originating from inadequate preliminary screening. Drum screen for wastewater treatment systems resolve this by removing 85-92% of TSS (Total Suspended Solids) at inflow points, preventing downstream equipment abrasion. Coarse screens in wastewater treatment plants specifically intercept debris larger than 6mm, reducing pump maintenance frequency by 40% compared to fine screens.
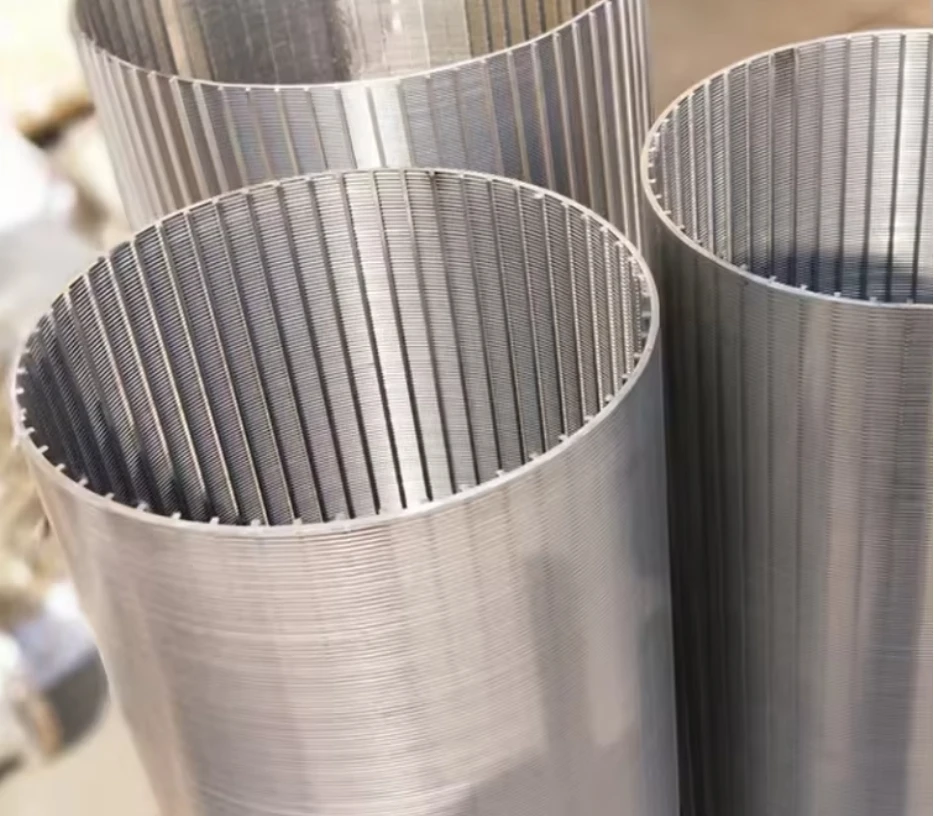
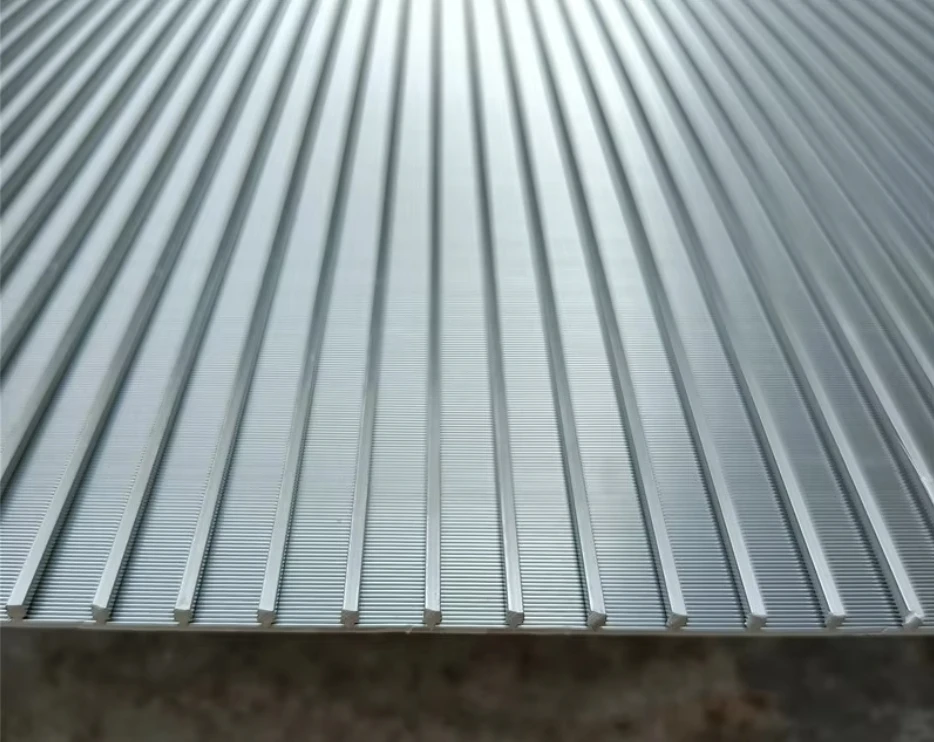
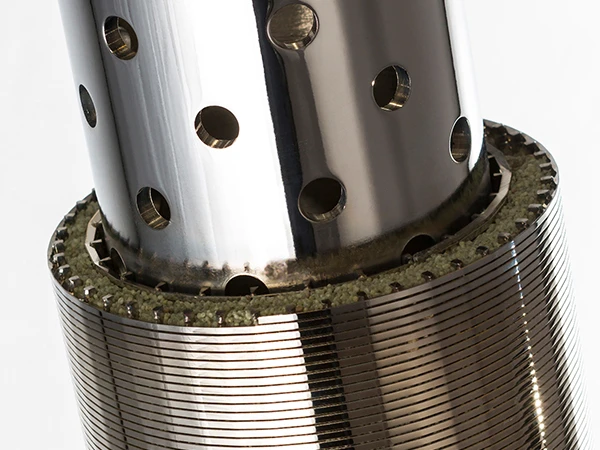
Engineering Excellence in Separation Technology
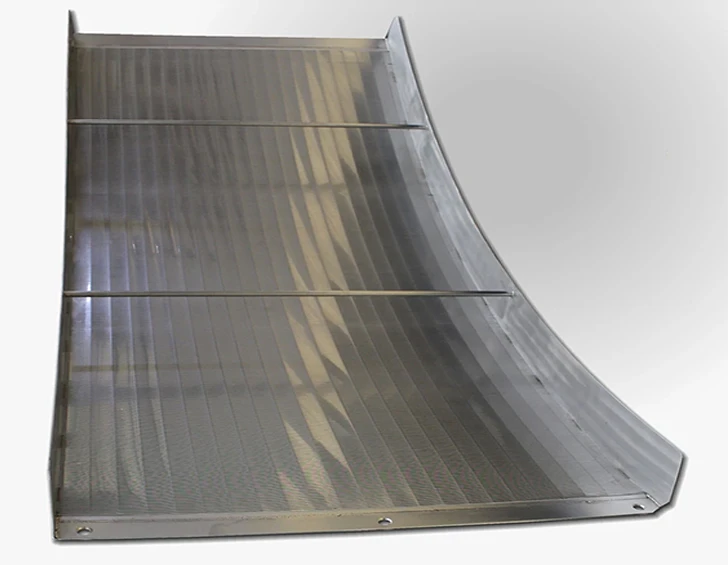
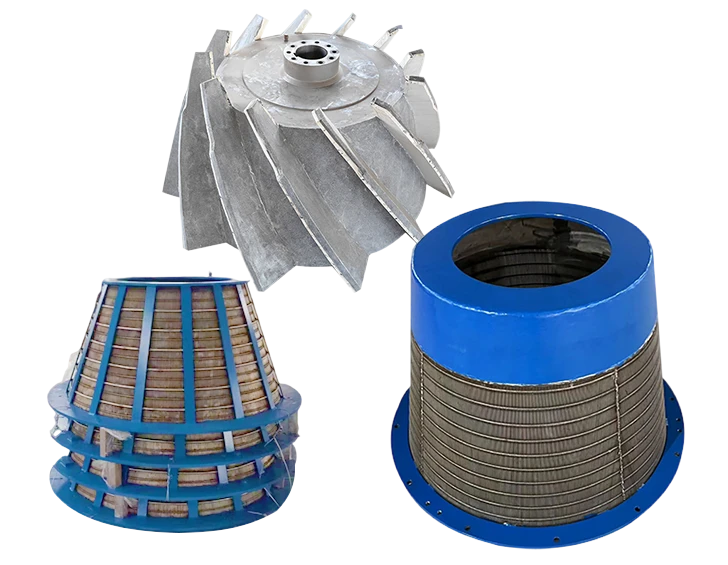
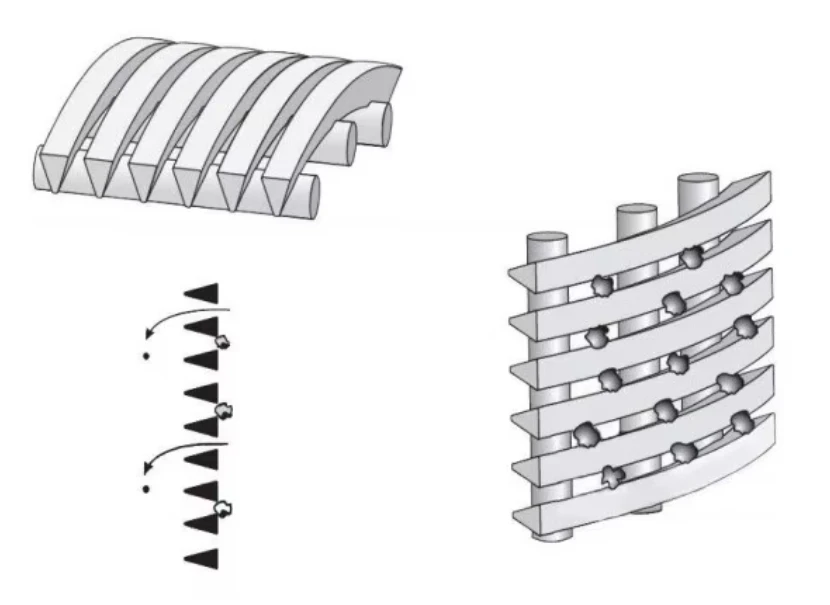
Advanced wedge wire screens demonstrate 0.2-3mm slot precision, achieving 94% capture efficiency. Rotating drum screens operate at 4-15 RPM with 0.75kW/1000m³ energy efficiency, outperforming static screens by 38% in flow consistency. Key innovations include:
- 316L stainless steel construction (150,000-hour corrosion resistance)
- Self-cleaning mechanisms reducing manual interventions by 73%
- Real-time torque monitoring (±2% accuracy)
Manufacturer Capability Analysis
| Vendor | Flow Capacity (m³/h) | Screen Opening | Material Grade | Energy Use |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Screening Tech Inc. | 12,000 | 0.5-6mm | 304 SS | 0.82 kW/1000m³ |
| EcoWater Solutions | 8,500 | 1-10mm | Duplex 2205 | 0.68 kW/1000m³ |
| PureFlow Systems | 15,000 | 2-12mm | 316L SS | 0.71 kW/1000m³ |
Tailored Configuration Strategies
Municipal plants typically require 3-6mm screens handling peak flows of 18m³/s, while food processing facilities opt for 1-3mm screens with CIP (Clean-in-Place) systems. Customization parameters include:
- Inclination angles (25°-35° for gravity-fed systems)
- Bypass weirs for stormwater surges (+35% capacity)
- Explosion-proof motors (ATEX Zone 1 compliance)
Operational Validation Through Projects
A Midwest wastewater plant achieved 91% RAS (Return Activated Sludge) quality improvement after installing 6mm drum screens, reducing clarifier cleaning from weekly to quarterly. Paper mill implementations show:
- 97.4% fiber recovery rate
- 22-month ROI through reduced belt press wear
- 0.5% downtime over 3-year operational period
Sustaining Peak Performance
Automated lubrication systems extend bearing life to 85,000 hours (vs. industry standard 60,000 hours). Predictive maintenance algorithms analyze vibration patterns with 89% fault detection accuracy, slashing unplanned outages by 67%.
Innovation Pathways for Wastewater Treatment Screens
Emerging screen technologies integrate AI-powered blockage prediction (92% accuracy rate) and graphene-coated surfaces showing 99% bacterial resistance. Facilities upgrading to smart screening systems report 31% energy savings and 19% longer equipment lifespan, positioning drum screen wastewater treatment solutions as essential infrastructure components.
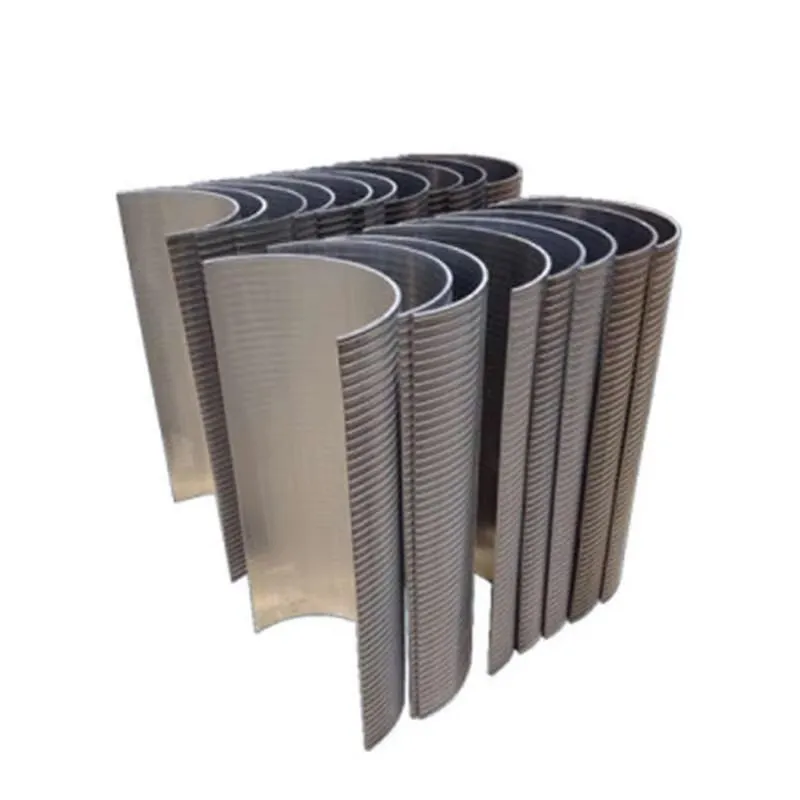

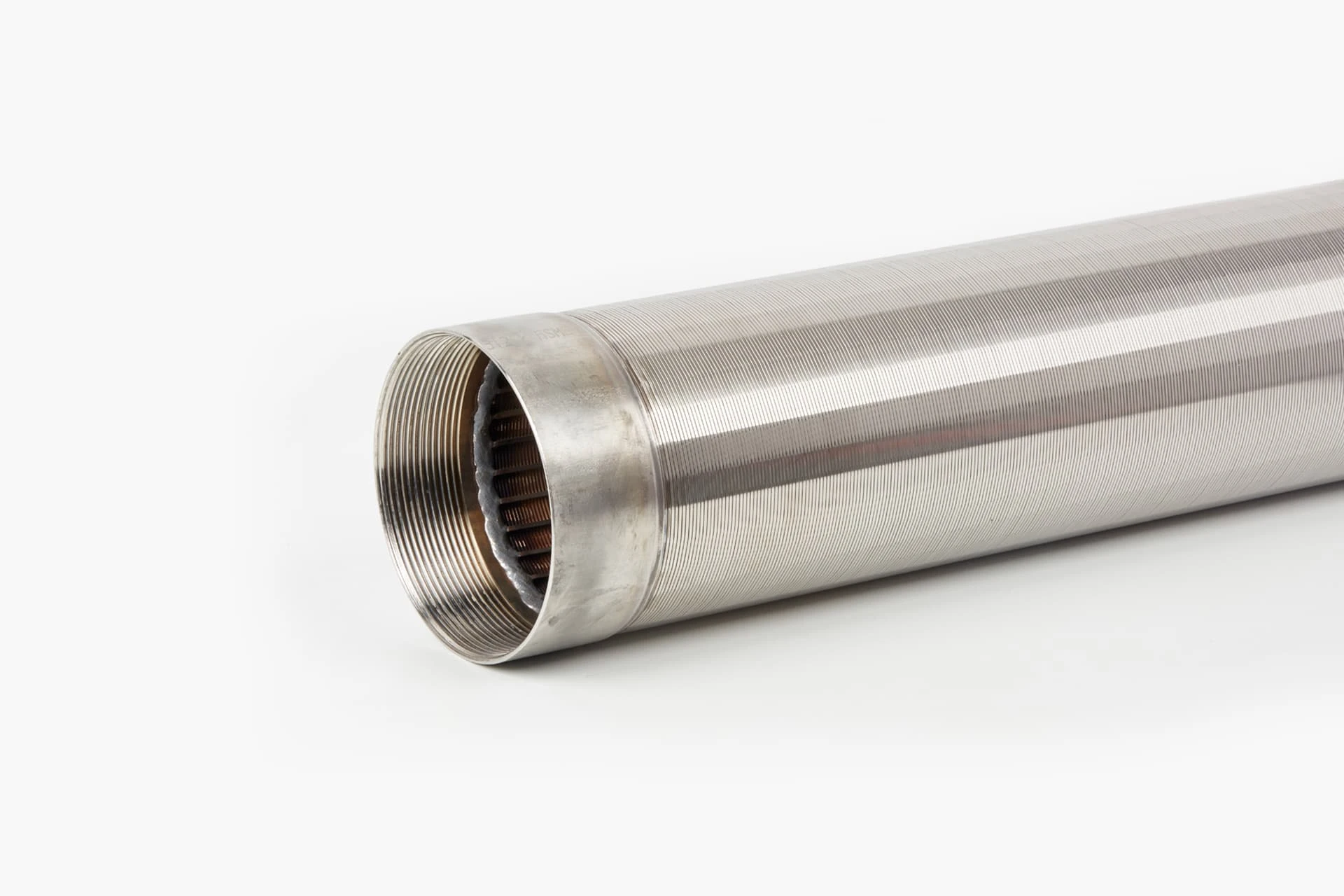
(wastewater treatment screen)
FAQS on wastewater treatment screen
Q: What is the purpose of a drum screen in wastewater treatment?
A: A drum screen removes large debris and solids from wastewater by rotating a cylindrical mesh. It prevents clogging in downstream processes and is ideal for high-flow applications.
Q: How does a coarse screen differ from other screens in wastewater treatment?
A: Coarse screens have larger openings (6-150 mm) to capture bulky materials like sticks and rags. They are typically used as the first filtration step, protecting finer screens and equipment from damage.
Q: What maintenance is required for wastewater treatment screens?
A: Regular cleaning to remove trapped solids, inspection for wear or corrosion, and lubrication of moving parts (e.g., drum screens) are essential. Automated systems often include self-cleaning mechanisms.
Q: Why are multiple screen types used in wastewater treatment plants?
A: Coarse screens handle large debris, while finer screens (e.g., drum screens) target smaller particles. Layered screening ensures efficient solids removal and protects sensitive equipment in later treatment stages.
Q: What factors determine the choice of screen in wastewater treatment?
A: Key factors include flow rate, particle size to be removed, space availability, and automation needs. Drum screens suit continuous operations, while coarse screens are cost-effective for initial filtration.