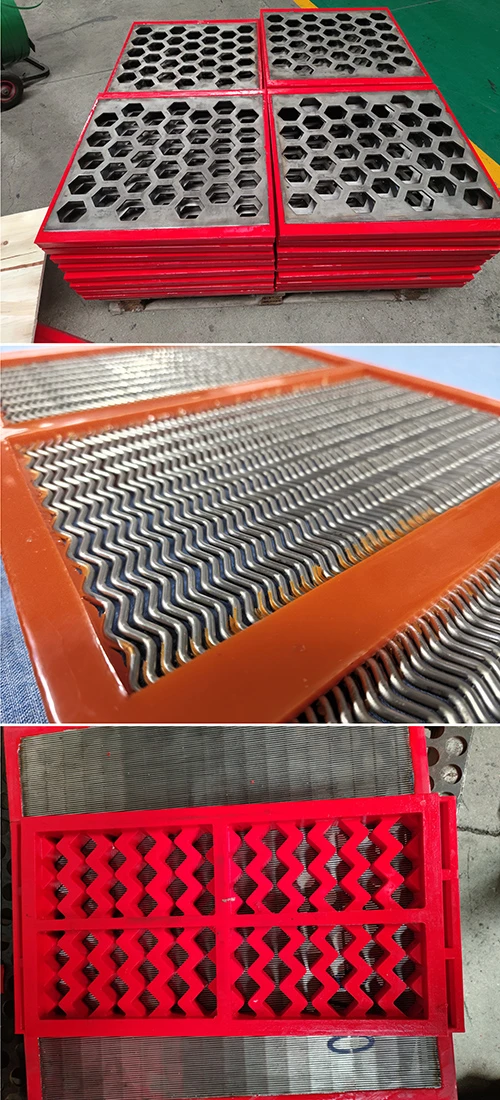
- Introduction to Perforated Screen Plates
- Technical Advantages and Material Innovations
- Comparative Analysis of Leading Manufacturers
- Customization Solutions for Diverse Applications
- Real-World Use Cases Across Industries
- Factors to Consider When Selecting a Supplier
- Future Trends in Perforated Plate Technology
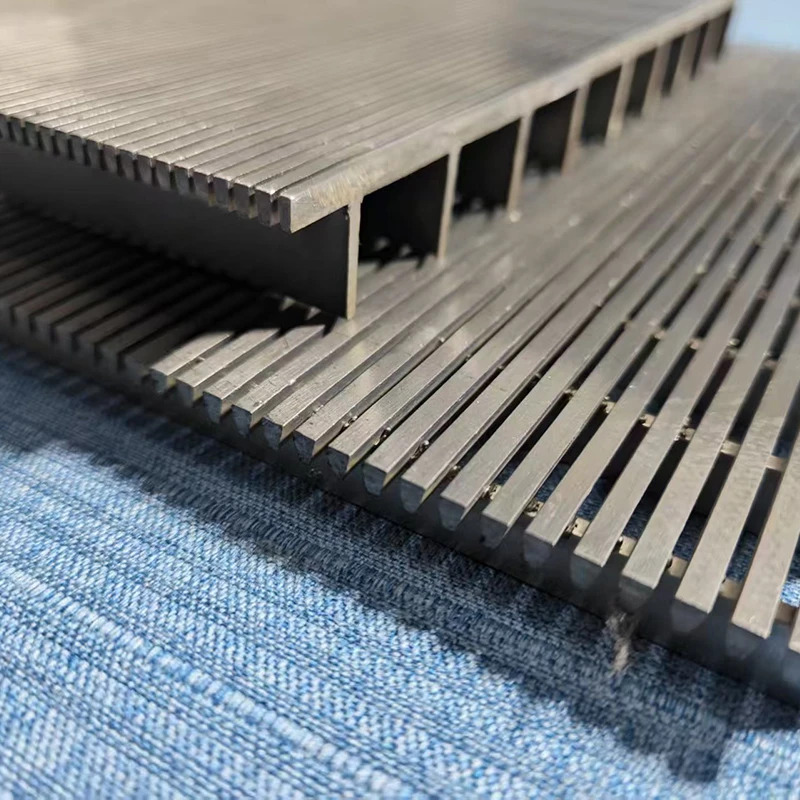
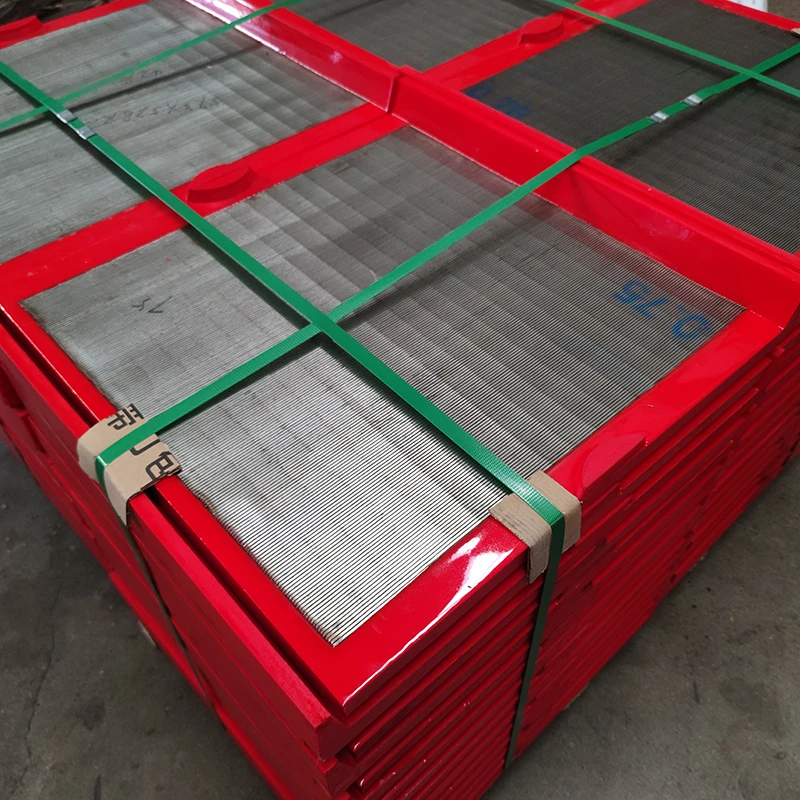
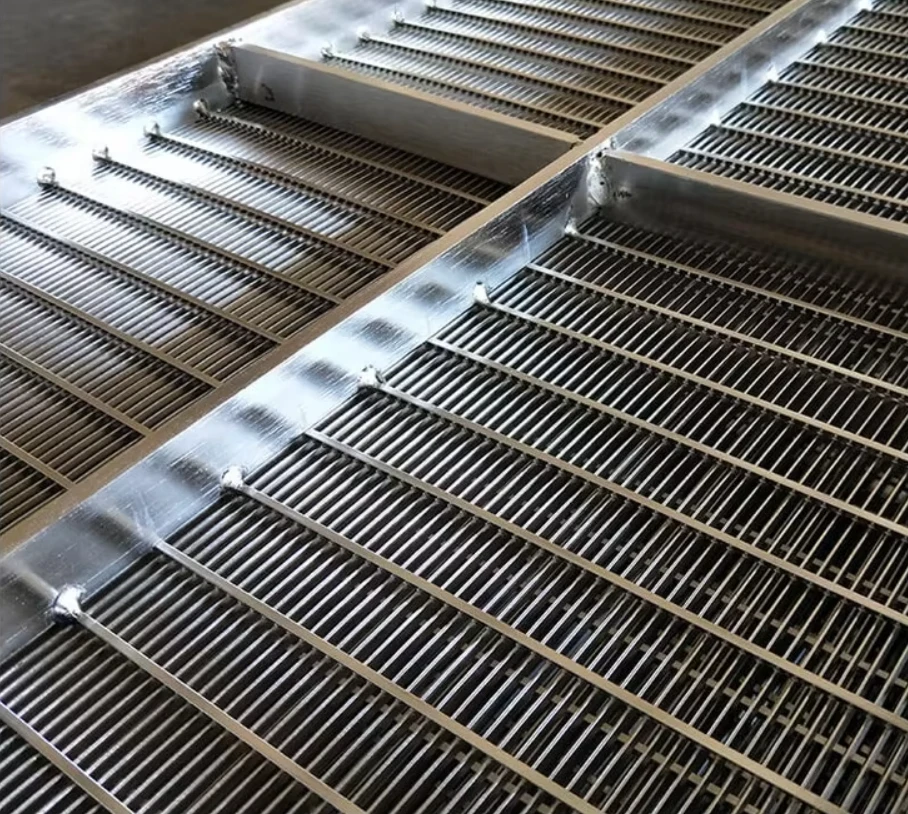
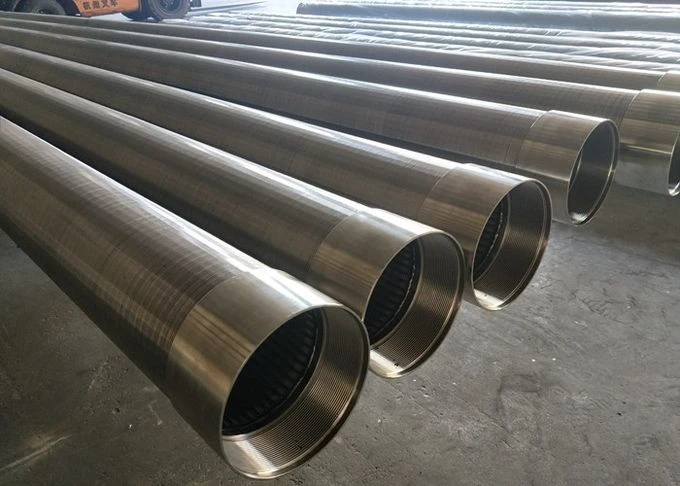
(perforated screen plate)
Understanding the Versatility of Perforated Screen Plates
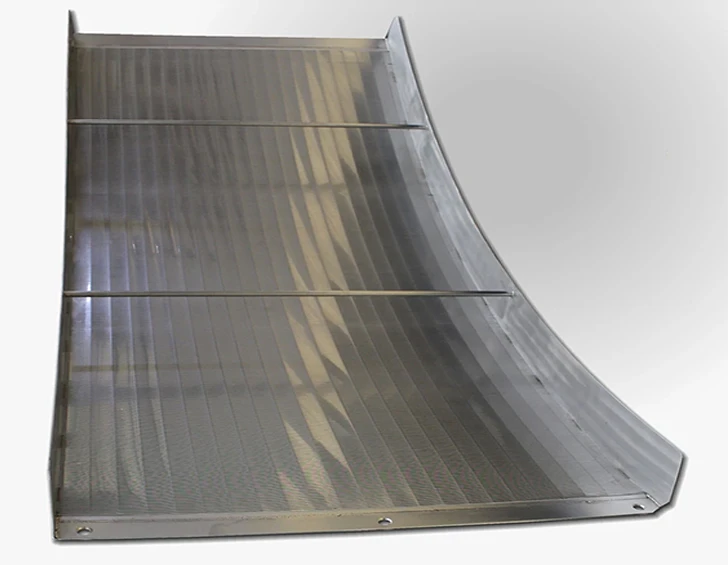
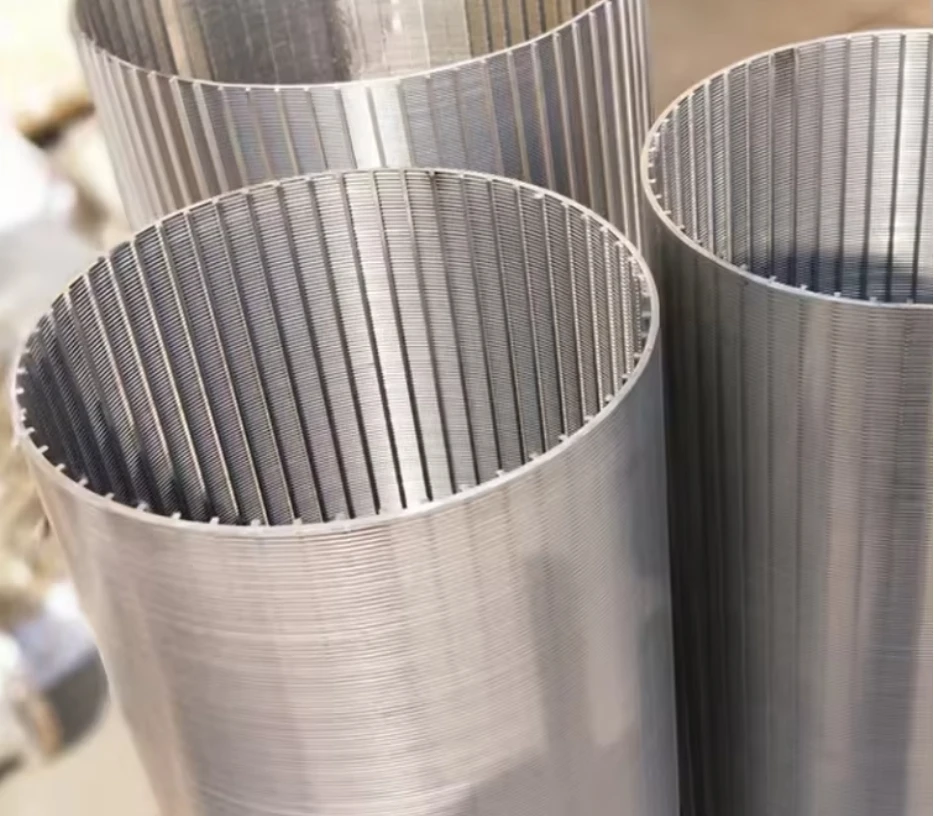
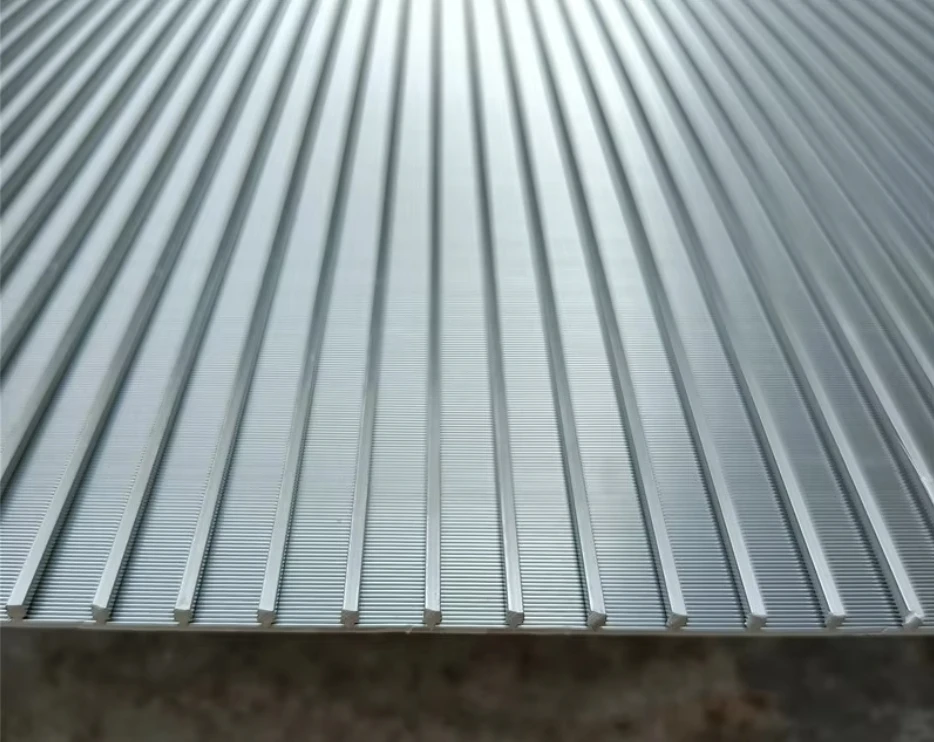
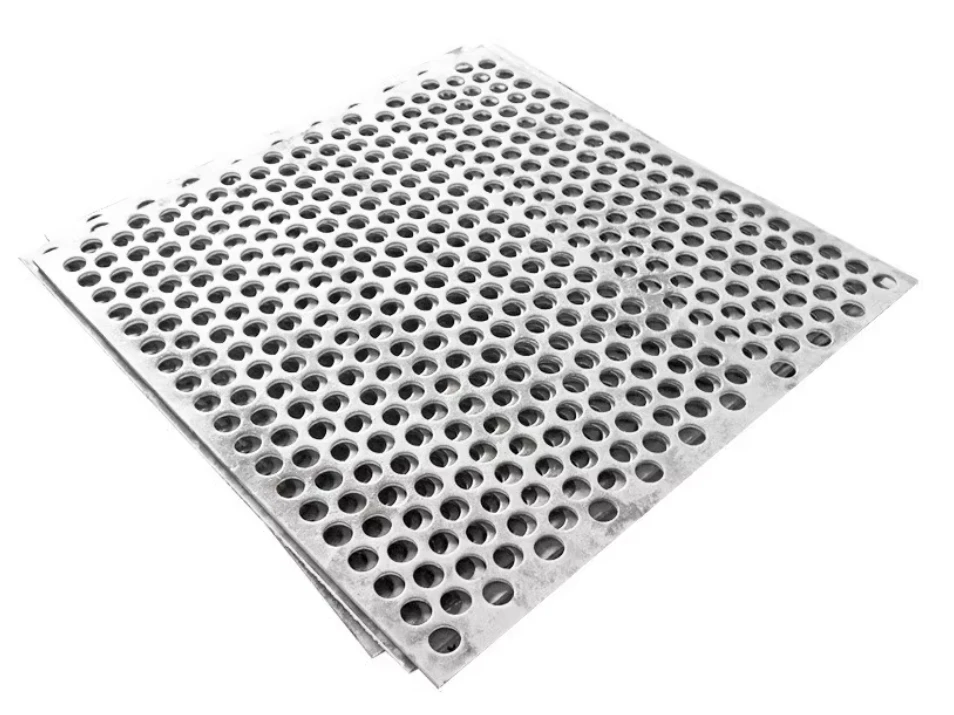
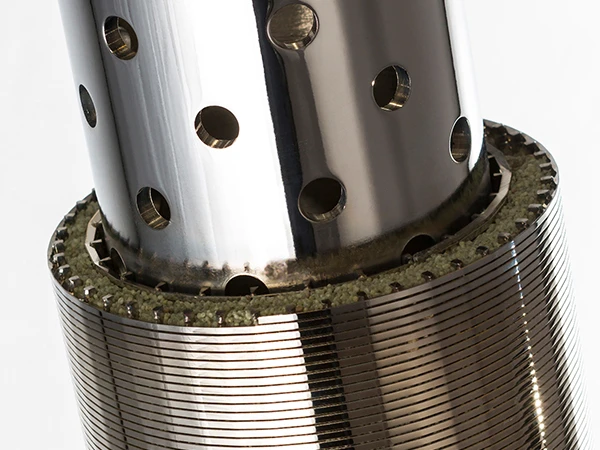
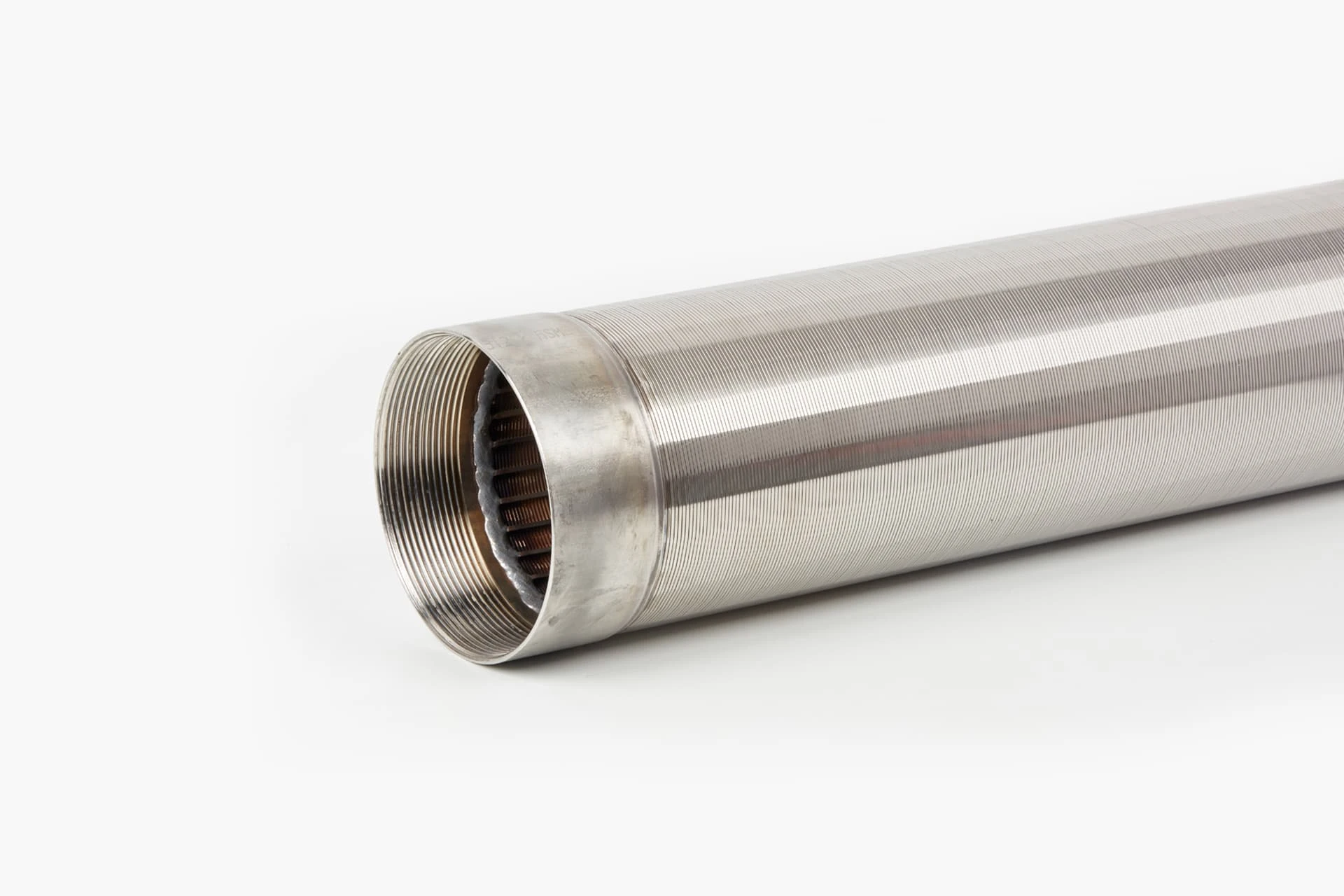
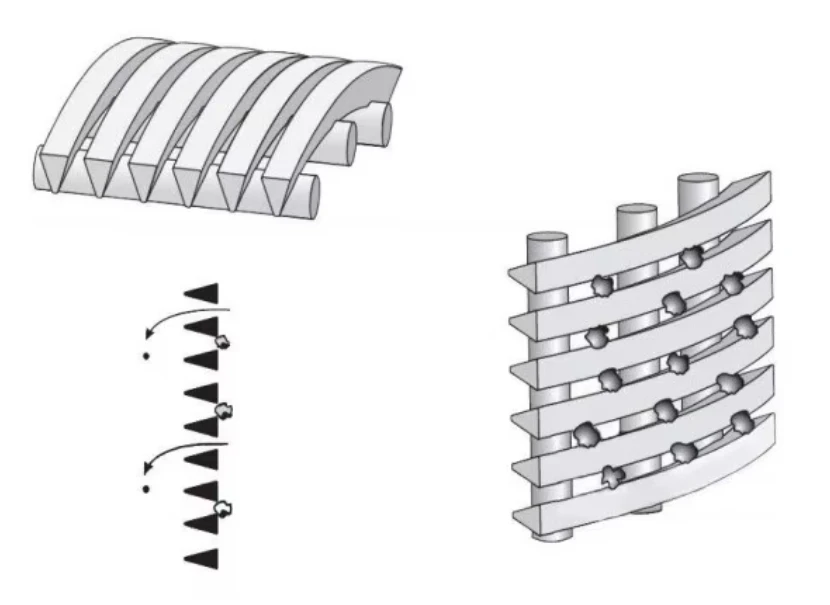
Perforated screen plates serve as critical components in industrial filtration, separation, and acoustic modulation systems. These precision-engineered panels, characterized by uniform hole patterns, enable optimal airflow while maintaining structural integrity. Modern manufacturing techniques allow hole diameters ranging from 0.3mm to 20mm, with open area ratios achieving up to 78% in standard configurations.
Engineering Excellence in Material Design
Advanced materials have redefined performance benchmarks:
- Stainless Steel 316L: 35% higher corrosion resistance vs. standard grades
- Polyurethane Hybrids: 82% improvement in abrasion resistance
- Laser-Cut Aluminum: ±0.05mm dimensional accuracy
Recent stress-test data reveals:
| Material | Load Capacity (psi) | Thermal Threshold (°F) | Cost Index |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Steel | 12,500 | 750 | 1.0 |
| 304 Stainless | 18,200 | 1500 | 2.3 |
| PU Composite | 8,750 | 250 | 1.8 |
Market Leaders in Manufacturing
Three manufacturers dominate the sector:
- Company A: 34% global market share
- Company B: 28% share with patented anti-clog tech
- Company C: 19% share specializing in custom patterns
Tailored Solutions for Operational Needs
Customization parameters include:
- Hole geometry (round, square, slot)
- Pattern density (15-85% open area)
- Edge finishing (hemmed, flanged, welded)
Industry-Specific Implementations
A food processing plant achieved 40% throughput increase using staggered-hole PU plates, while an automotive OEM reduced acoustic leakage by 22dB through hexagonal-pattern screens.
Selecting Optimal Perforated Screen Solutions
Critical evaluation factors:
- Flow rate requirements (200-50,000 CFM)
- Particulate size distribution
- Chemical exposure levels
Innovations Shaping Perforated Plate Applications
Emerging technologies integrate smart sensors directly into plate structures, enabling real-time monitoring of pressure differentials. Sustainable manufacturing methods now reduce material waste by up to 65% compared to traditional processes.
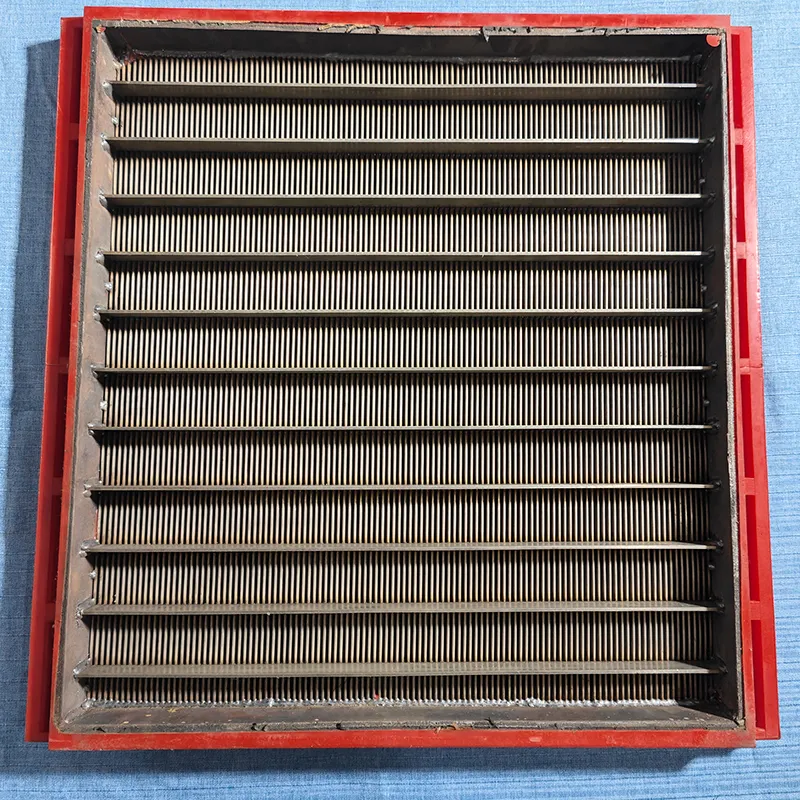

(perforated screen plate)
FAQS on perforated screen plate
Q: What are the primary applications of a perforated screen plate?
A: Perforated screen plates are widely used in filtration, sorting, and separation processes across industries like mining, agriculture, and wastewater treatment. Their precise hole patterns enable efficient material classification. They are also utilized in acoustic and ventilation systems.
Q: How does a perforated plate screen differ from a PU plate?
A: A perforated plate screen is typically made of metal (e.g., stainless steel) and used for heavy-duty screening, while a PU plate (polyurethane) offers flexibility and wear resistance for finer particle separation. PU plates are quieter and better for corrosive environments. Both serve distinct roles based on material and operational needs.
Q: What advantages do perforated screen plates offer in industrial settings?
A: Perforated screen plates provide durability, high flow-through rates, and customizable hole designs to match specific process requirements. They reduce clogging risks and are easy to clean. Their robust construction ensures long-term cost-effectiveness.
Q: Can perforated plate screens be customized for specialized machinery?
A: Yes, perforated plate screens can be tailored in hole size, shape, and spacing to suit equipment like vibrating screens or conveyor belts. Materials (metal or PU) and thickness are also adjustable. Customization enhances efficiency in sorting or filtering applications.
Q: How do I maintain a PU plate used as a screening component?
A: Clean PU plates regularly with water or mild detergents to prevent material buildup. Inspect for wear or tears, especially in high-abrasion environments. Proper storage away from UV exposure and extreme temperatures prolongs their lifespan.