- Overview of screening in wastewater treatment
- Performance data and efficiency metrics
- Technical design advancements
- Comparative manufacturer analysis
- Custom engineering solutions
- Industry deployment case studies
- Future innovations and conclusion
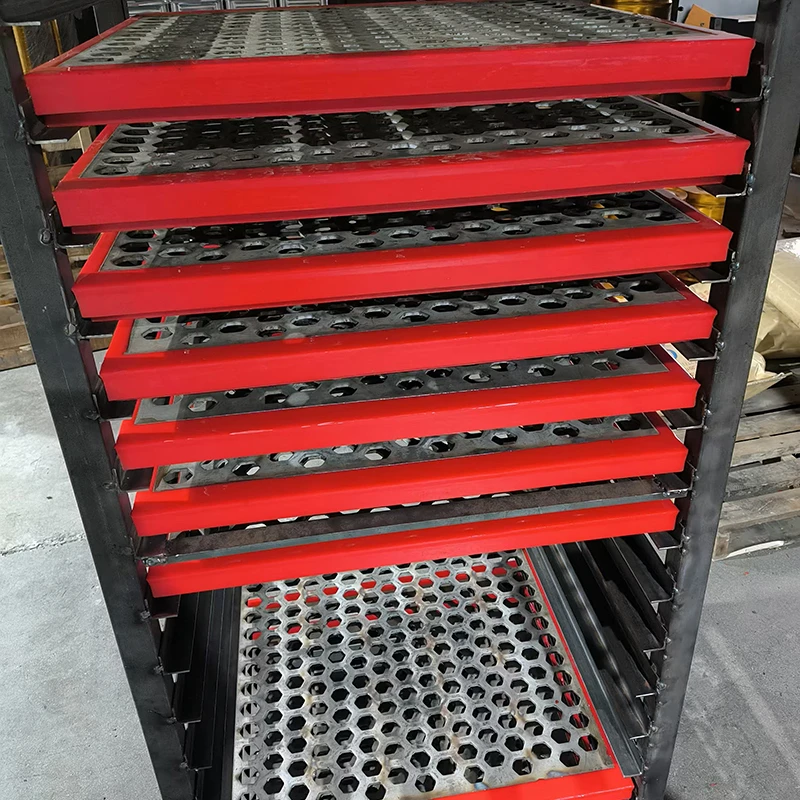

(wastewater screens)
Essential functions of bar screens in wastewater treatment facilities
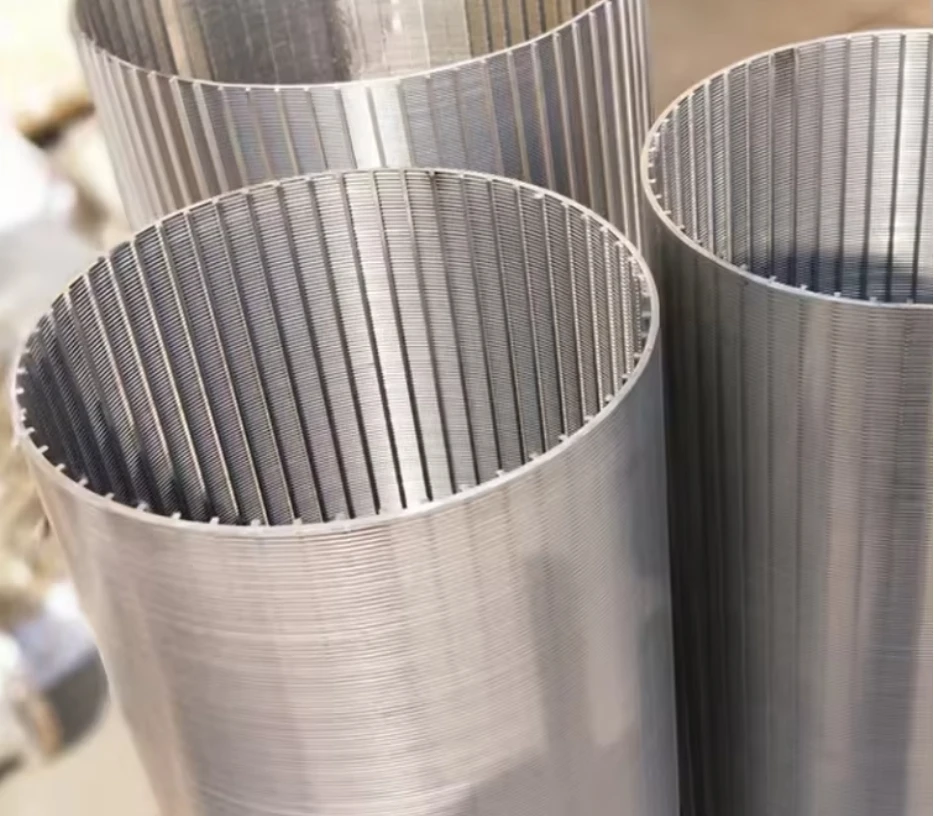
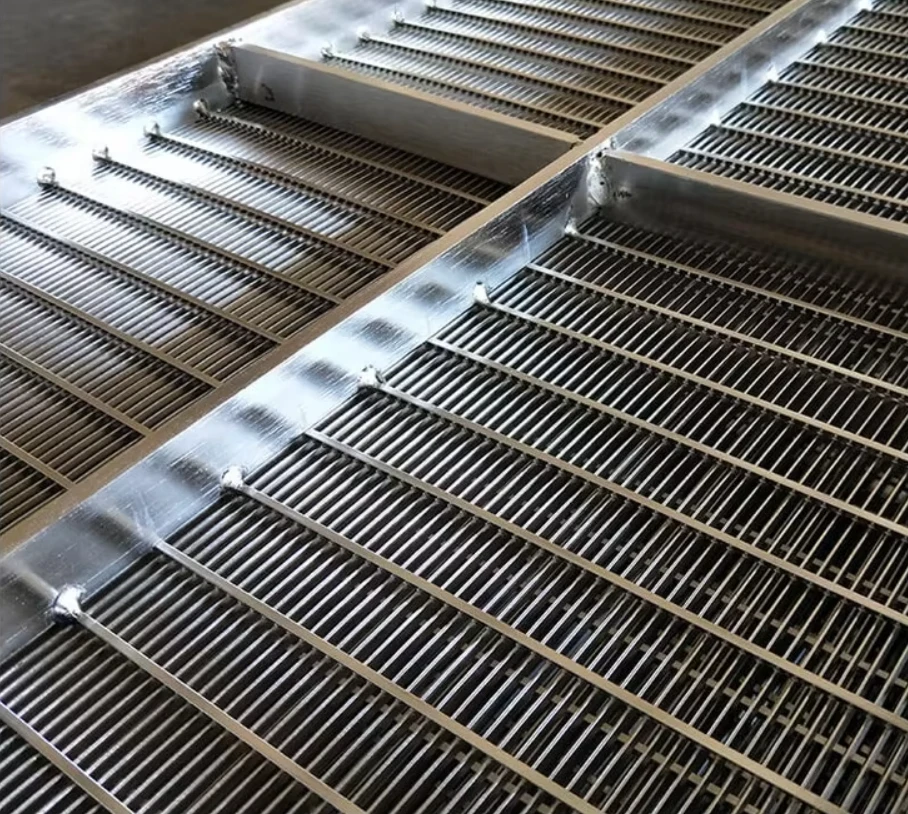
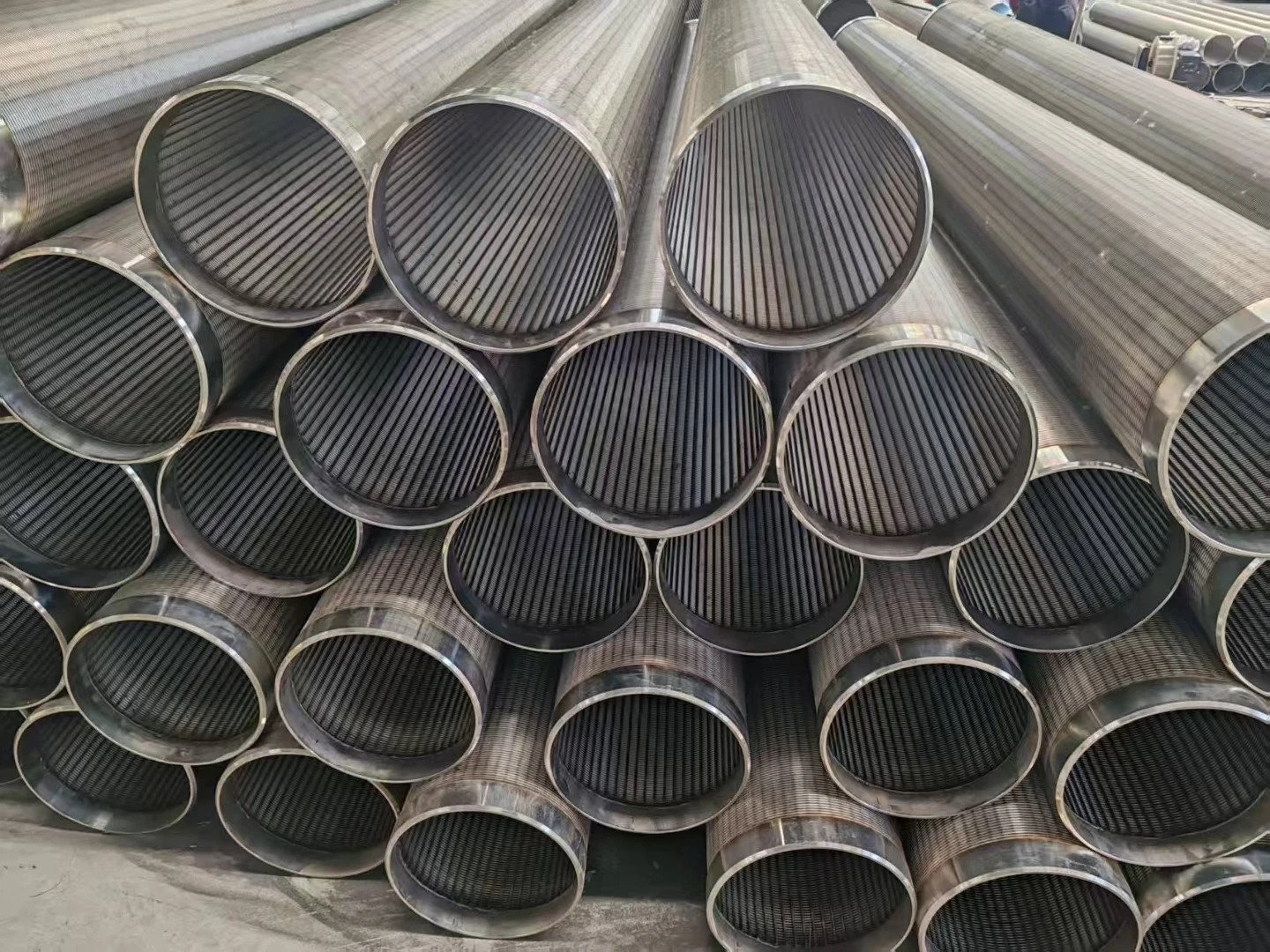
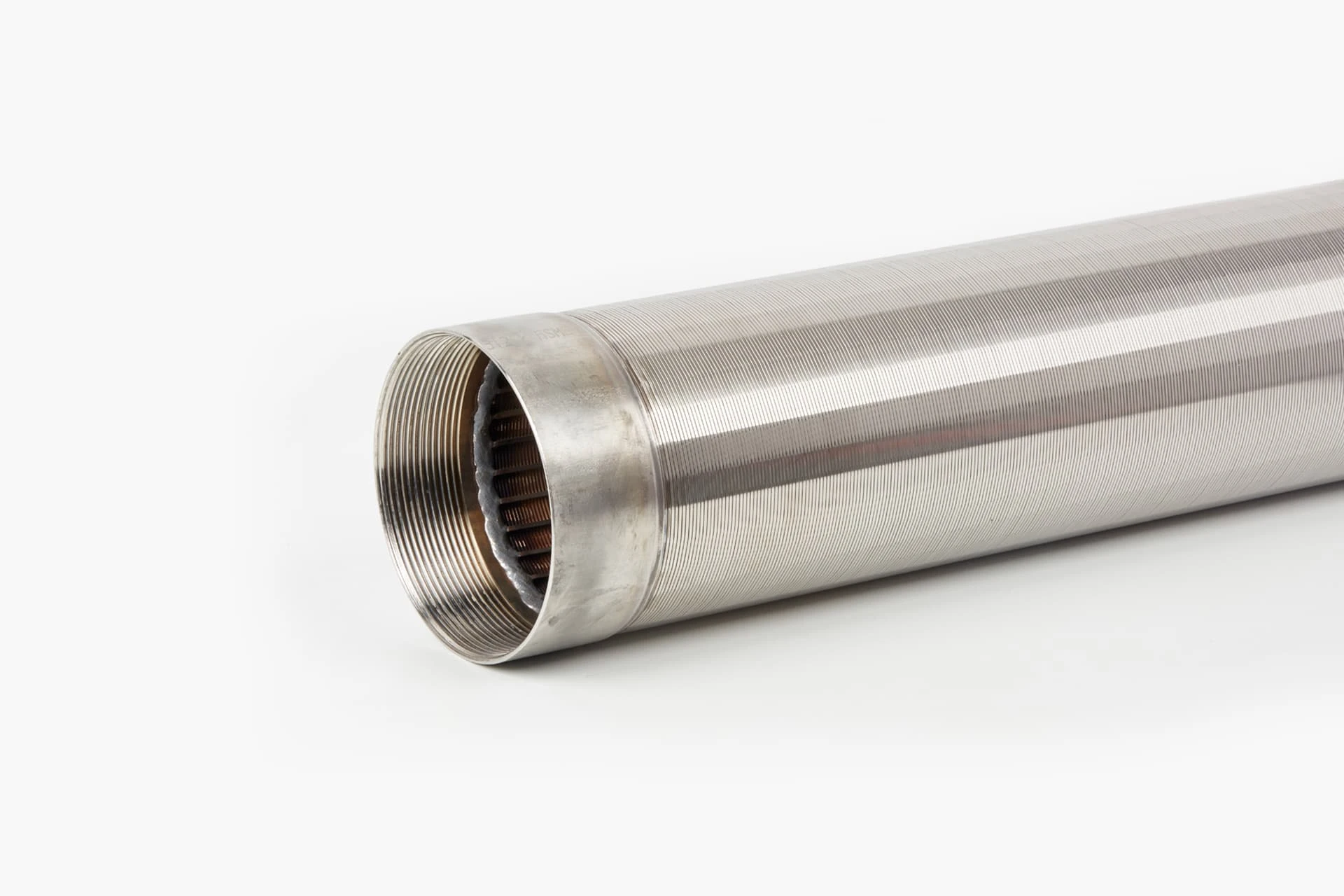
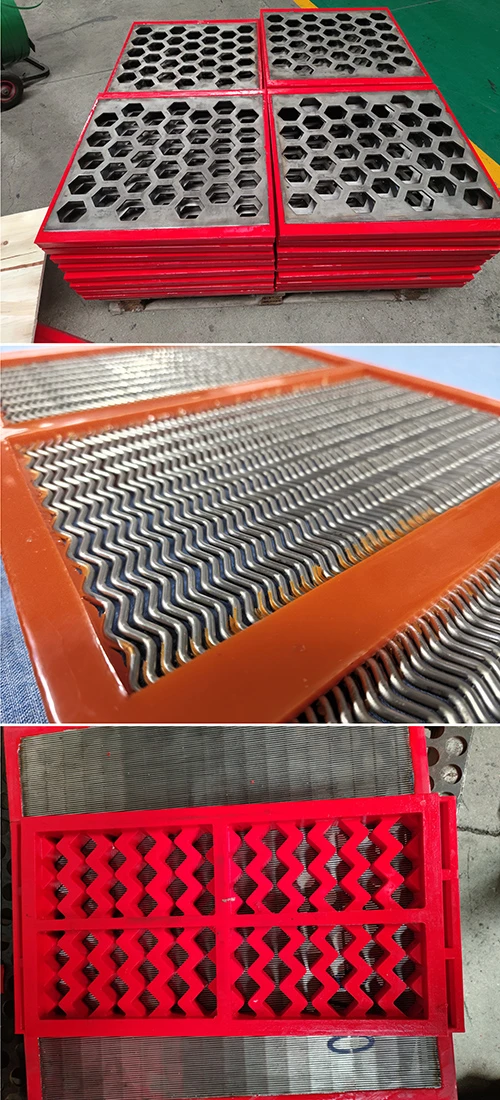
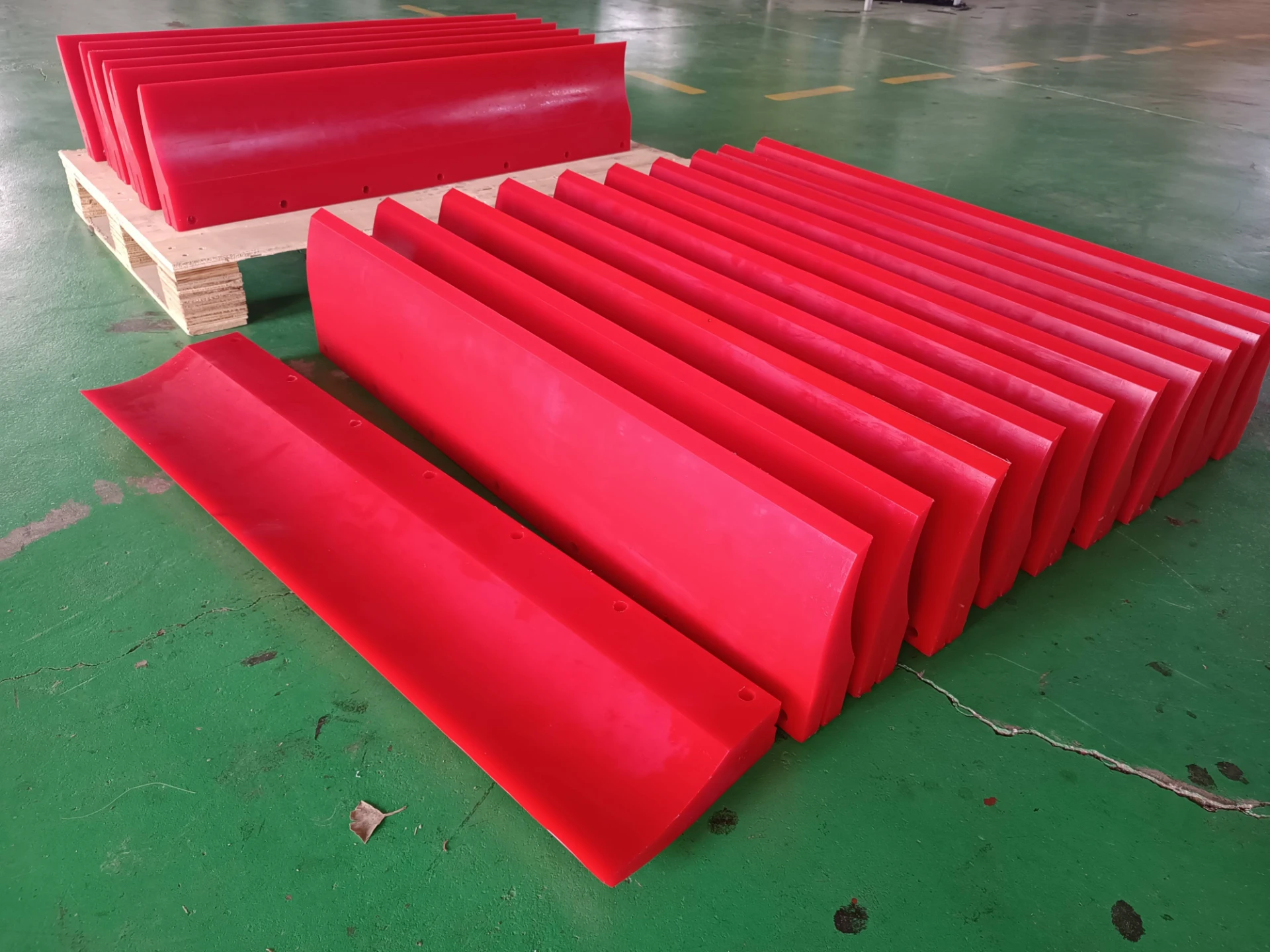
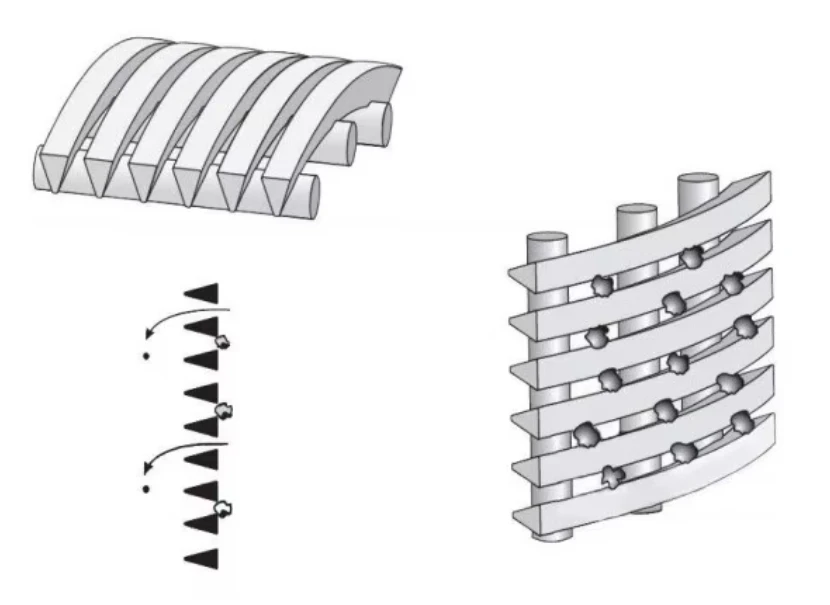
Screening units serve as the primary defense in wastewater management, capturing solids before downstream processes. Modern facilities deploy varying screen configurations based on flow dynamics, particle sizes exceeding 6mm, and processing volumes. Headworks protection prevents pump blockages and reduces sedimentation in channels. Selection between coarse bar racks and fine mesh variants depends on the plant's tertiary treatment requirements. Material composition typically involves 316 stainless steel for corrosion resistance in harsh sewage environments. Automated raking mechanisms maintain hydraulic efficiency through continuous debris removal cycles.
Operational efficiency and performance benchmarks
Studies verify that optimized screening captures 97.8% of solids above 10mm sieve size, substantially lowering downstream maintenance. Flow tolerance data demonstrates consistent operation at peak rates of 650 million gallons daily without bypass scenarios. Power consumption metrics reveal modern parabolic screen wastewater models operate at 35% lower kilowatt-hour consumption compared to conventional designs. Processing validation under controlled conditions shows particle retention rates:
| Screen Aperture | Capture Rate | BOD Reduction |
|---|---|---|
| 10mm | 97.8% | 12.4% |
| 6mm | 99.1% | 14.7% |
| 3mm | 99.6% | 18.2% |
These metrics prove critical for operations reducing mechanical wear on pumps by nearly 40% through efficient macro-solid extraction.
Engineering breakthroughs in filtration technology
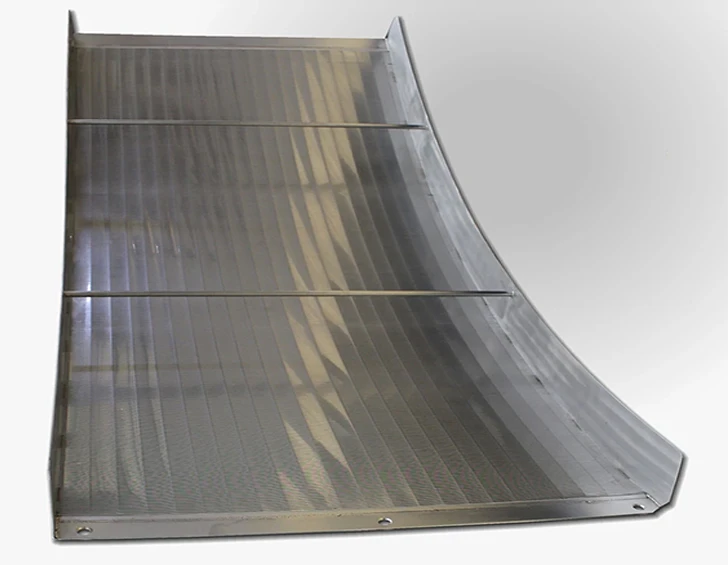
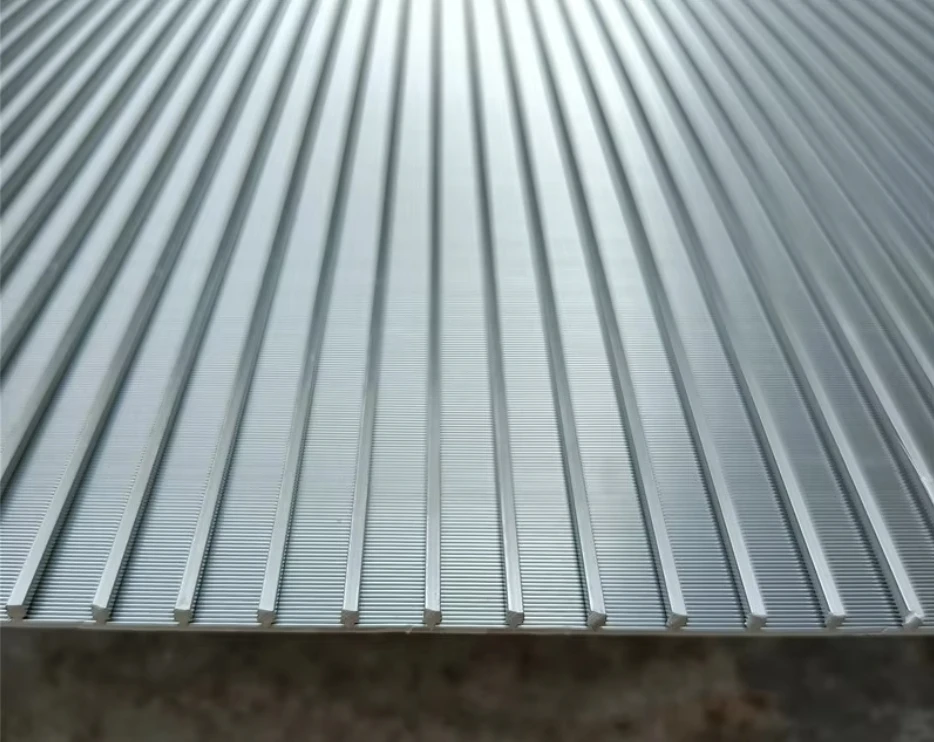
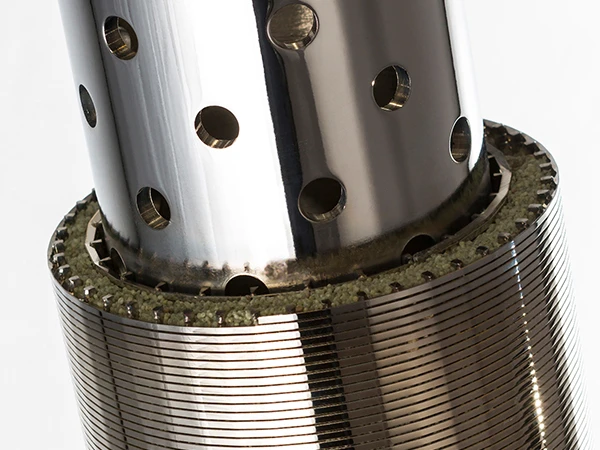
Hydrodynamic modeling enables screen curve optimization that maintains constant velocity profiles, increasing capture efficiency while reducing screenings carryover. Advanced parabolic screen wastewater configurations feature self-cleaning mechanisms eliminating manual raking operations. Rotating belt designs integrate with grit removal systems for comprehensive preliminary treatment. Enhanced features include automated differential pressure sensors triggering optimized cleaning cycles and integrating with SCADA systems. Dual-shaft grinders incorporated downstream achieve particle fragmentation below 3mm without damaging mechanical components.
Commercial landscape and specification comparison
Leading manufacturers exhibit distinct capabilities across technical parameters:
| Supplier | Opening Range | Max Flow | Screenings Capture | Maintenance Interval |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Supplier A | 3-25mm | 750 MGD | 99.3% | 10,000 hours |
| Supplier B | 5-30mm | 525 MGD | 98.7% | 7,200 hours |
| Supplier C | 2-20mm | 480 MGD | 99.1% | 8,400 hours |
Key purchase considerations include rotational velocity thresholds maintaining solids retention during surge events and harmonic dampers reducing vibrational stress on mounting structures.
Site-specific adaptation capabilities
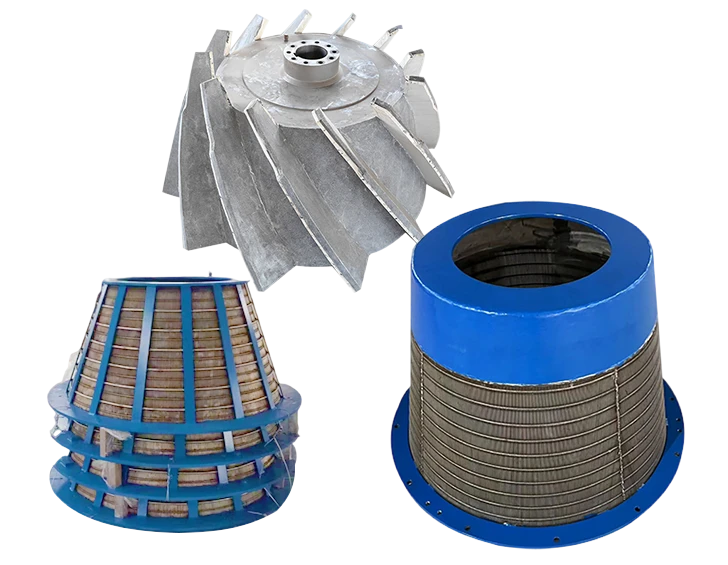
Customized configurations overcome unique installation constraints like variable channel inclinations exceeding 45° or fluctuating influent compositions. Specialized rake geometries handle fibrous materials prevalent in industrial effluents without jamming incidents. Corrosion protection upgrades involve duplex stainless steel construction for coastal facilities experiencing saline infiltration. Integration packages combine screening units with compactors achieving 70% volume reduction before landfill transport. Controls programming accommodates operational variables including monsoon-season flow tripling and extreme temperature fluctuations.
Municipal and industrial implementation examples
Baltimore's Back River facility processed 180 million daily gallons using step-type screens that reduced organics loading by 22%. Petrochemical plants in Texas achieved zero bypass incidents despite hydrocarbon concentrations exceeding 800 ppm by installing specialized parabolic screen wastewater units. Scandinavian installations demonstrated uninterrupted performance at -25°C through geothermal heating elements integrated into screening channels. Municipal reports confirmed 18% reduction in downstream clarifier sludge volumes following fine screen upgrades with 2mm perforated panels.
Evolutionary trends shaping wastewater screens
development
Screening technology evolves toward adaptive artificial intelligence systems that predict maintenance needs through solids accumulation pattern recognition. Emerging materials like ceramic-metal composites promise extended service life in abrasive conditions. Integrated wastewater screens now interface with plant-wide process controls automatically adjusting operation based on real-time BOD fluctuations. Modular designs accelerate installation timelines by 65% while accommodating existing infrastructure constraints. These innovations position screening as the cornerstone for sustainable wastewater management infrastructures globally.
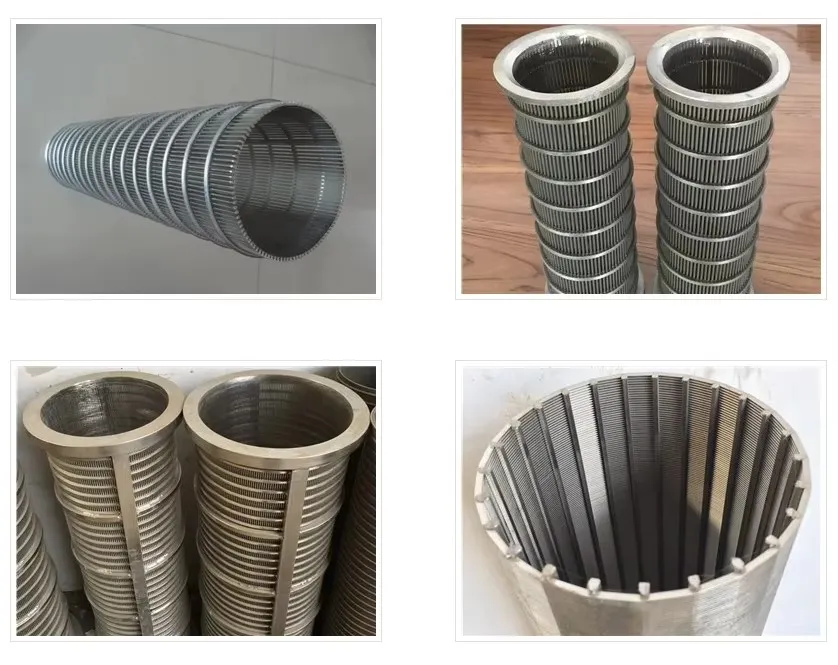

(wastewater screens)