- Introduction to Perforated Metal and Its Industrial Significance
- Technical Advantages Over Traditional Materials
- Comparative Analysis of Leading Manufacturers
- Customization Options for Diverse Applications
- Real-World Case Studies Across Industries
- Sustainability and Long-Term Performance Metrics
- Future Trends in Perforated Metal Solutions
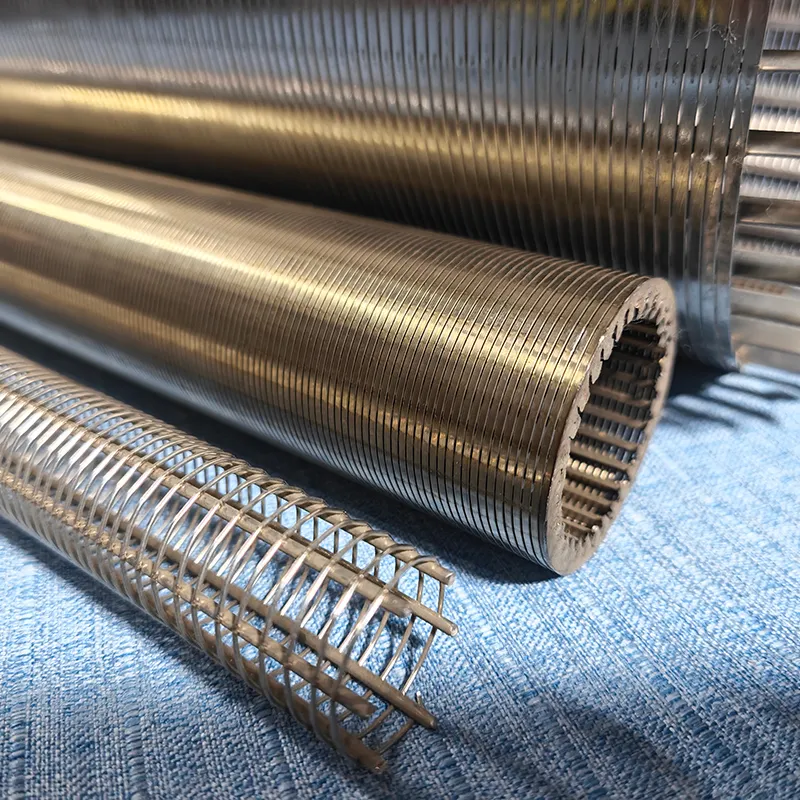

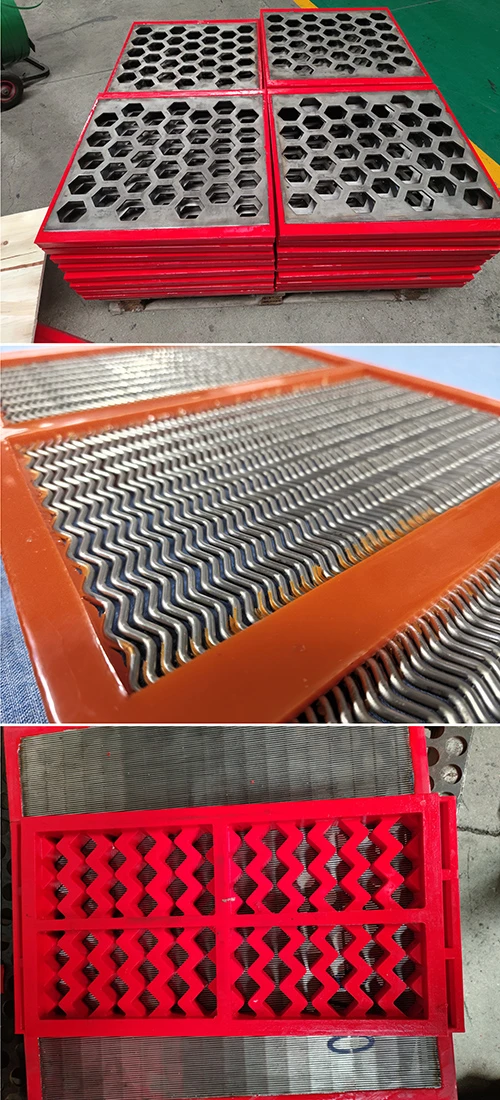
(perforated metal)
Understanding Perforated Metal and Its Industrial Significance
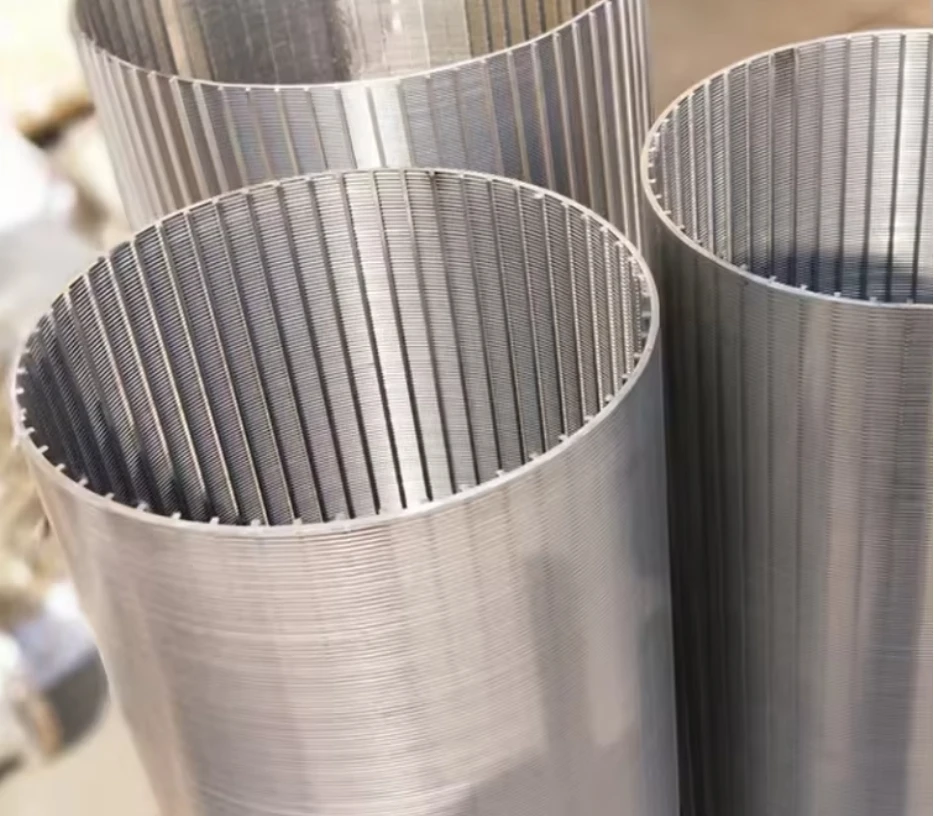
Perforated metal, characterized by precisely patterned holes in sheets or panels, has become indispensable across architecture, manufacturing, and infrastructure. With a global market growth rate of 6.8% CAGR (2023–2030), this material combines functionality with aesthetic flexibility. From perforated metal
screens enhancing airflow in HVAC systems to perforated metal panels enabling modern façade designs, its applications demonstrate versatility unmatched by solid-surface alternatives.
Technical Advantages Over Traditional Materials
Engineered perforations reduce material weight by 15–40% while maintaining structural integrity, as evidenced by ASTM E8 tensile testing results:
| Material | Thickness (mm) | Hole Pattern | Weight Reduction | Load Capacity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel 304 | 2.0 | Round, staggered | 32% | 420 MPa |
| Aluminum 6061 | 1.5 | Square, linear | 28% | 275 MPa |
| Galvanized Steel | 3.0 | Hexagonal | 37% | 550 MPa |
Advanced laser-cutting techniques achieve ±0.1 mm tolerance, enabling complex geometries for acoustic damping (NRC 0.75–0.95) and precision filtration (up to 99.8% particulate retention).
Comparative Analysis of Leading Manufacturers
The competitive landscape reveals distinct specialization areas:
| Manufacturer | Material Range | Hole Size (mm) | Production Speed | MOQ | Certifications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MetalTech | 15 alloys | 0.5–50 | 120 m²/hr | 50 m² | ISO 9001, LEED |
| PrecisionPerf | Stainless steel only | 0.3–30 | 85 m²/hr | 10 m² | AS9100D |
| EcoFab | Recycled metals | 1–100 | 60 m²/hr | 100 m² | Cradle to Cradle |
Third-party testing shows MetalTech’s stainless sheets withstand 2.5× industry-standard corrosion resistance in salt spray tests (ASTM B117).
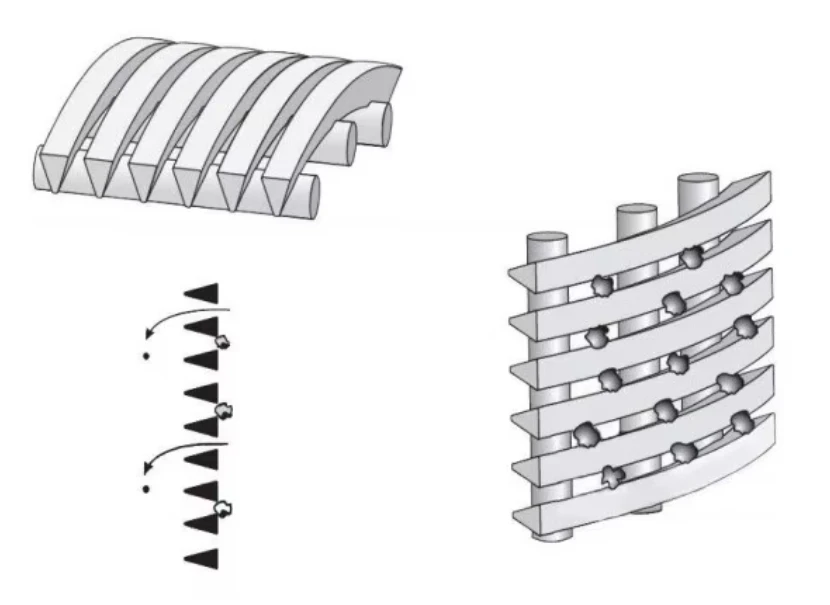
Customization Options for Diverse Applications
Modern fabrication systems enable:
- Variable hole densities (5–95% open area)
- Multi-axis formed profiles (up to 150° bends)
- Hybrid materials (metal-polymer composites)
A recent automotive project achieved 22% weight reduction in door panels using variable-perforation aluminum sheets without compromising crash-test ratings.
Real-World Case Studies Across Industries
Architecture: The Sydney Axiom Tower utilized 8,500 m² of triangular-perforated aluminum panels to reduce solar heat gain by 40%, cutting HVAC energy use by 18% annually.
Manufacturing: A German auto plant implemented curved perforated metal screens in robotic workcells, decreasing particulate contamination by 93% while maintaining 360° equipment visibility.
Sustainability and Long-Term Performance Metrics
Lifecycle analyses demonstrate 65–80% recyclability rates for perforated metals versus 45–60% for composite alternatives. Powder-coated versions maintain reflectivity above 85% after 25 years of UV exposure (ASTM G154).
Innovating with Perforated Metal Solutions
Emerging applications include 3D-printed titanium perforated panels for aerospace (38% lighter than machined parts) and conductive perforated metal sheets enabling EMI shielding up to 120 dB at 10 GHz frequencies.
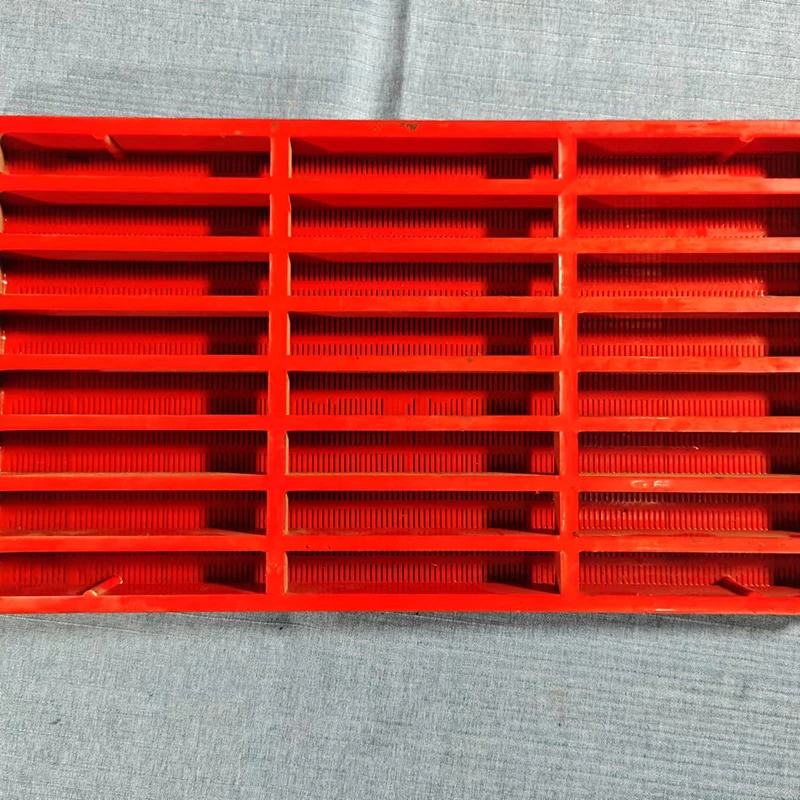

(perforated metal)
FAQS on perforated metal
Q: What are the common applications of perforated metal sheets?
A: Perforated metal sheets are widely used in architectural facades, industrial filtration systems, and decorative screens. Their customizable hole patterns allow for airflow, light diffusion, and aesthetic design. They are also ideal for machinery guards and acoustic panels.
Q: How do perforated metal screens enhance building ventilation?
A: Perforated metal screens promote natural airflow while reducing direct sunlight, improving energy efficiency. They maintain structural integrity and privacy without compromising visibility. Their durability makes them suitable for both indoor and outdoor installations.
Q: What factors determine the cost of perforated metal panels?
A: Costs depend on material type (e.g., stainless steel, aluminum), hole size/shape complexity, and panel thickness. Additional treatments like powder coating or galvanization also affect pricing. Custom designs typically incur higher costs than standard patterns.
Q: Can perforated metal panels provide noise reduction?
A: Yes, perforated metal panels with specialized acoustic backing absorb sound waves in spaces like theaters or offices. The hole pattern and panel depth influence noise reduction levels. Combined with insulation materials, they achieve high Sound Transmission Class (STC) ratings.
Q: How durable are perforated metal sheets in outdoor environments?
A: Made from corrosion-resistant materials like aluminum or galvanized steel, they withstand harsh weather and UV exposure. Proper coatings further enhance longevity. Minimal maintenance is required compared to wood or plastic alternatives.